Between constant emails and robust patient databases, interprofessional communication in healthcare is growing increasingly complex. A Sermo survey revealed that over 31% of providers feel ill-equipped to train staff in emerging technologies—but these technologies are central to modern healthcare communications. On top of this, physicians must navigate regulatory, economic and cultural shifts, which all impact care coordination.
In this article, we’ll cover the current communications landscape, detailing barriers, methods and tips.

4 Reasons why communication is important in healthcare
About 68% of Sermo’s community of physicians communicate with other doctors at least once per week. The effectiveness of these conversations directly affects patient safety, clinical decision-making and patient satisfaction.
Here are the impacts of frequent, positive communication:
1. Patient safety
Sermo polls report that 63% of patients rank their safety as the top priority when it comes to communication in healthcare—and physicians share this view.
The Joint Commission attributes 60% of adverse events in hospitals to communication challenges. Similarly, researchers from the University of Bern and the University Hospital of Cologne associate poor communication with increased surgical complications and mortality rates. And effective communication systems facilitate the urgency, accuracy and clarity necessary to ensure patient safety.
2. Improved decision-making
Information exchanges that involve all key stakeholders—including everyone from physician assistants to surgeons—contribute to improved clinical decision-making across the continuum of care.
On the role of multidisciplinary teams in effective decision-making, Adam Hetz, PA-C and Sermo member, noted, “As a physician assistant, I’ve witnessed firsthand the invaluable contributions that APPs make in filling critical gaps in care delivery. Our adaptability combined with our advanced training positions us to address emerging healthcare challenges and provide innovative solutions to meet the needs of our patients.”
3. Improved job satisfaction
Physicians who have positive working relationships report higher rates of career satisfaction. This applies to both positive intra- and inter-professional relationships. The opposite is also true: Care silos can make physicians feel overworked and undersupported.
4. Improved patient satisfaction
The connection between effective communication and patient satisfaction extends beyond patient safety. It also strengthens continuity of care, providing emotional support, promoting treatment adherence and fostering overall trust in healthcare providers.
As one Pediatrician and Sermo member put it, “Effective communication in healthcare provides good relationships and good teamwork and these help to improve patient satisfaction.”
Interested in getting communication tips from fellow healthcare professionals? Connect with over 1 million physicians worldwide and share your experiences on the topics that matter to you.
“Effective communication in healthcare provides good relationships and good team work and these help to improve patient satisfaction.”
Sermo, Pediatrician

Barriers to communication in healthcare
Certain healthcare communications challenges are new. Others are a reflection of longstanding systemic issues. These barriers include:
Absence of integrated and compatible systems
A pressing, major healthcare challenge is bridging the two-way interoperability gap between medical apps and electronic health record (EHR) systems. Health IT systems are often incompatible with both internal and external systems, which can lead to underutilization and misuse. Non-interoperability also causes one-way communication and missed or delayed inclusion of allied health recommendations. Insufficient staff training further exacerbates this problem.
Lack of values-based collaboration
According to one Sermo survey, APPs most often describe their working relationship with physicians as collaborative, supportive and professional. Developing this type of collaboration is among the core communication skills for healthcare professionals.
But coordination between medical professionals isn’t always streamlined. Communication gaps can occur for the following reasons:
- Different understandings of “collaboration”
- Omission of allied health input from discharge summaries
- Ambiguity in roles and responsibilities
- Limited direct time communicating with patients and reliance on junior staff for discharge
- Fragmented or incompatible technology systems
When asked how physicians could better support them day-to-day, 22% of APPs sought more collaboration in patient management, 19% wanted greater knowledge sharing and 18% requested regular feedback on patient care—all of which require communication.
Absence of a dedicated care coordinator
Physicians often have heavy workloads that limit their available time to communicate comprehensively with inter- and intra-disciplinary care teams. This time constraint can result in missed or delayed information, which adversely affects patient care outcomes. That’s why multiple studies point to the need for a dedicated liaison—whether a social worker, nurse, or allied health professional—to bridge the gap between care teams.

Types of communication in healthcare
Collaboration is about more than formal meetings and verbal communication. Here are some of the common communication strategies in healthcare:
- Face-to-face: Face-to-face communication involves both in-person and remote video meetings or discussions. While the literature indicates that direct meetings are the most effective means of communication, it’s generally recognized as a secondary method because it’s less convenient.
- Written: The same study as above indicates that written communication is currently the primary method of communication among physicians. Referral and discharge letters are the most common forms.
- Email: Email is less common because physicians cite concerns about privacy, security and potential increases in workload. They also note its potential for medico‐legal liability.
- Structured electronic documents: Structured electronic documents are standardized and systematically include relevant patient information. While care teams benefit from their standardization, teams risk overlooking allied health input.
- Shared EHRs: The majority of physicians use EHRs. Two-thirds (66%) of primary care physicians say they’re satisfied with their current EHR system, while 18% report strong satisfaction.
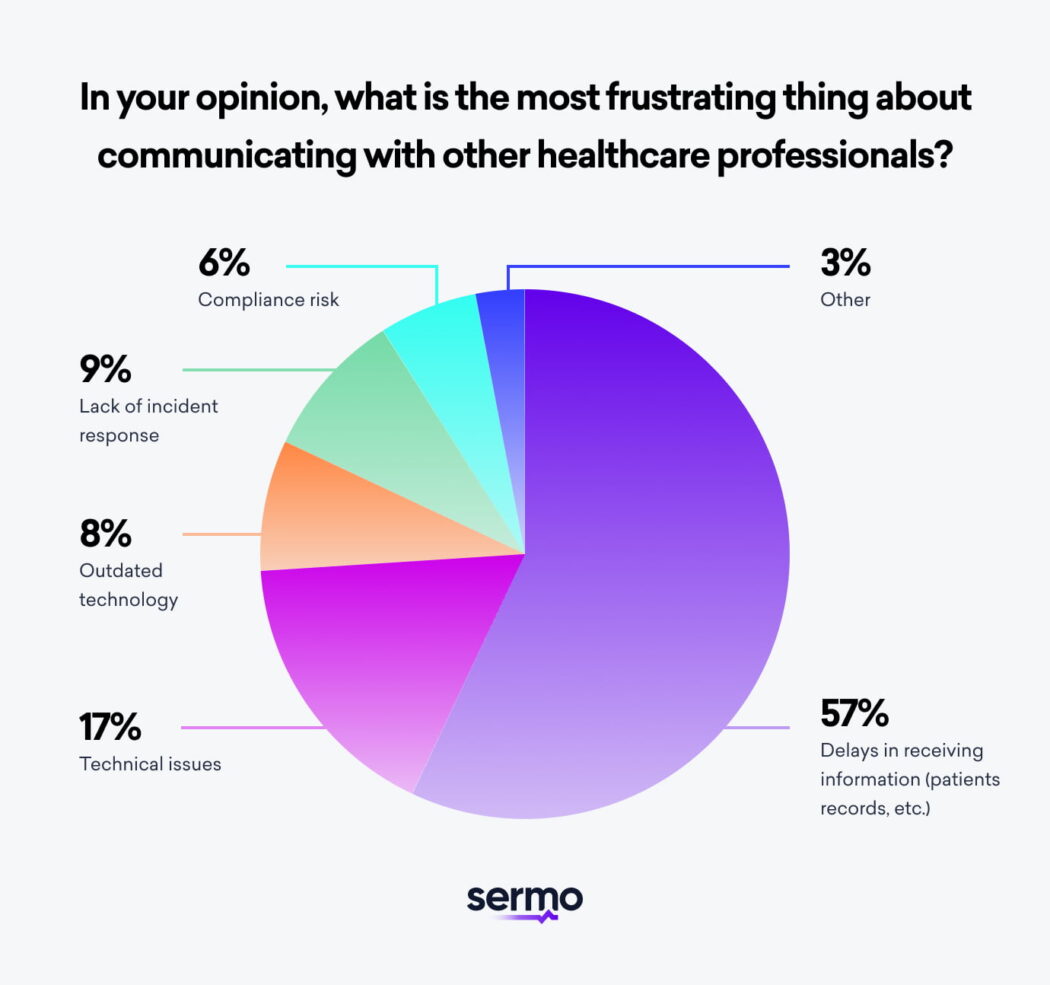
Sermo asked its members what the most frustrating part of communicating with other physicians is, and 57% reported delays in receiving information. EHRs’ capacity to reduce delays is effective, yet technologists are actively refining systems to improve interoperability.
Improving interoperability is a foremost industry priority. According to a Sermo survey of 100 U.S.-based healthcare leaders, 36% cited integration with their existing systems as an ongoing challenge, while 33% reported difficulties achieving interoperability with other healthcare facilities and networks.
4 ways to improve communication healthcare for professionalsSermo polls report that 63% of patients rank
Here are tips to ensure system interoperability, build your communication skills and support functional care coordination.
1. Ensure data liquidity
Prioritize systems that export patient data in widely accepted standardized formats, like CCD/C-CDA, and integrate external data. This lets you create and maintain comprehensive, longitudinal patient records.
2. Prioritize data security
Compliance risks and technical issues are core communication problems—both of which concern sensitive patient data. Increase the security of your communications systems through:
- Physical safeguards: Install high-definition security cameras at all access points, restrict entry to server rooms with biometric or keycard systems and use backup generators to maintain uptime.
- Administrative safeguards: Develop and enforce comprehensive data handling policies, provide regular training to employees on compliance and appoint a Chief Information Security Officer.
- Technical safeguards: Deploy robust firewalls and encryption protocols, implement network address translation to conceal internal IP addresses and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA).
3. Support team-based care
Many EHRs don’t allow team members to enter data or perform tasks in accordance with their licensure or privileges. If you have the power to do so, update your EHR system—or consider investing in the necessary infrastructure—to make sure all key stakeholders can directly contribute information to the record.
In supporting team-based care, consider how hierarchies impact collaboration and patient care outcomes. Researchers from the University of Michigan associate breakdowns in healthcare communication with hierarchical gaps, reluctance to challenge authority and role ambiguity. These factors can undermine the free flow of critical patient information.
4. Join a professional social network
Learn how other physicians approach interprofessional communications by joining a professional social network like Sermo. Social media can be a good choice—but dedicated platforms designed for physicians are a step better. These networks keep you up to date on relevant trends and technologies, collaborate with peers and solve common communication challenges.
Join a global network of physicians
Sermo surveyed its community of physicians to learn what motivated them to pursue medicine. Almost half (46%) said, “I just wanted to help others.” But communication challenges can inhibit physicians’ ability to serve their local community.
That’s why it’s beneficial to join a network of physicians who share your challenges and concerns. As one Sermo member from Colombia put it, “I got a lot of help from colleagues from all around the world, it was very amazing.”
Sermo is the largest global online platform, where doctors connect on the topics that matter to them and their patients—and have a few laughs along the way. Become a Sermo member today.