Global Survey of 1,150+ Healthcare Professionals Examines Expert Perspectives on Weight Loss Medications and their Evolving Role on Patient Outcomes
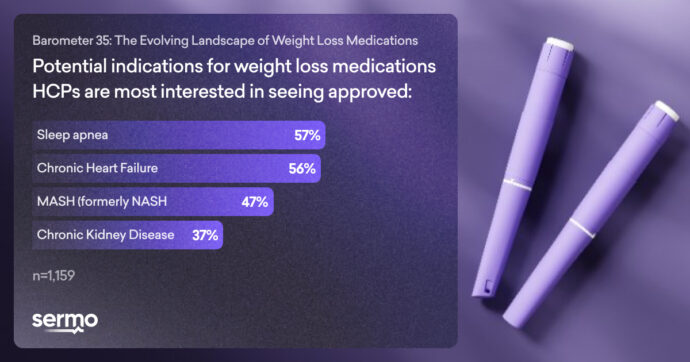
New York – The 35th Barometer from Sermo, a fast, frictionless HCP social engagement platform and leader in healthcare insights, revealed that healthcare providers (HCPs) are most eager to see GLP-1 medications be approved to treat sleep apnea. The Barometer surveyed 1,150+ global healthcare providers across specialties on their experience prescribing weight loss medications. In addition to sleep apnea, HCPs were most interested in seeing GLP-1 medications approved to treat chronic heart failure and MASH (formerly NASH).
Patients Taking Medication Dosage Into Their Own Hands:
According to the LA Times, “some patients, with or without the help of doctors, are experimenting with “microdosing” weight loss drugs — using smaller-than-recommended amounts — in order to stretch limited supplies, reduce costs, and even potentially curb side effects.”
- 91% of surveyed HCPs reported they are somewhat to very concerned about patients independently adjusting their prescribed medication doses.
- 75% of those who actively prescribe weight loss medications have had patients report side effects (in line with results from Sermo Barometer 31, October 2023 at 77%).
- The most common side effects patients report are nausea (55%), diarrhea (12%), and stomach pain (9%).
- Only 20% of HCPs reported that patients stopped taking medications because of side effects.
- 69% of HCPs report patients very often to often inquire about the cost of weight loss medications.
How are Celeb Endorsements & Non-traditional Healthcare Settings Prescribing GLP-1s Impacting Patients?
- 78% of HCPs surveyed report that Hollywood, celebrities, and influencers’ embrace of GLP-1s for weight loss has harmed patients’ realistic expectations of the medication.
- 72% of HCPs believe non-traditional healthcare programs such as med spas and telemedicine companies prescribing weight loss medications are problematic.
- 71% reported lack of adequate patient education as the top concern followed by improper patient monitoring (65%) and lack of familiarity with side effects (52%).
- Only 11% of surveyed HCPs felt very confident in these non-traditional healthcare settings’ competency levels to manage weight loss medications.
- Due to recent reports of severe side effects associated with GLP-1 medications half (58%) of HCPs reported making changes in their practices to monitor patients more closely.
“The expanding role of GLP-1 medications beyond weight loss, such as their potential to treat conditions like sleep apnea or chronic heart failure, represents an exciting shift in healthcare. For primary & family care, this evolution offers immense potential to address complex, interrelated conditions more effectively. However, it also underscores the need for comprehensive training and systems to support safe prescribing practices and close patient monitoring. As these therapies evolve, primary care will be at the forefront of integrating them into holistic, patient-centered management,” said Dr. Kyle Lee, BMLSc, BMBS, MPH, CCFP, Sermo Medical Advisory Board Member.
Weight Loss Treatment Doesn’t Stop at GLP-1s:
- Two-thirds (67%) of HCPs report increasing metformin prescriptions for patients who don’t qualify for GLP-1s.
- Semaglutide medications are still the most popular weight loss medication to prescribe with 82% reporting they actively prescribe Ozempic, 65% reporting they actively prescribe Wegovy, and 37% prescribing Rybelsus.
Weight-Loss Care Trends: Certifications, Mental Health, and the Push for Oral GLP-1s:
- Certifications: Despite 81% reporting prescribing any medications for weight loss or a weight loss benefit in the past year, 67% of those surveyed report not having any Obesity Treatment Certification, such as the American Board of Obesity Medicine (ABOM) or European Association Study of Obesity Medicine (EASO)
- Impact on Mental Health: After metabolic health (35%), 16% of HCPs report mental health as a top area of improvement for patients who have been on weight loss medications for at least six months followed by self-esteem at 12%.
- Oral is the future: HCPs believe that oral medications are the future of GLP-1 medications, with 78% reporting that they think the majority of patients will want to switch to an oral form once available.
- Weight-Loss Goal Management: Only a third (33%) of HCPs are gradually weaning patients off weight loss medications once they’ve achieved their goal weight and less than a third (31%) are prescribing lower doses once the weight goal has been achieved.
This survey was fielded from November 20th – 22nd, 2024 as the 35th edition of Sermo’s ongoing Barometer study. The survey included 1,159 global healthcare professionals whose specialties ranged from PCPs, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, cardiologists, endocrinologists, OBGYNs, and pediatric medicine. To explore more findings, visit: https://app.sermo.com/barometer
About Sermo:
Sermo is a fast, frictionless physician engagement platform providing the healthcare industry with real-time business insights and authentic physician touchpoints through our global community of 1M+ healthcare professionals and state-of-the-art technology. For over 20 years, Sermo has been turning physician experience, expertise, and observations into actionable insights that benefit pharmaceutical companies, healthcare partners, and the medical community at large. To learn more, visit www.sermo.com.
Media Contact:
Allyson Noonan
allyson.noonan@gmail.com
(858) 245- 7256